The Industrial Model: Revolutionizing Architectural Design

The landscape of architecture is ever-evolving, driven by innovation, technology, and the need for sustainability. Among the myriad of approaches reshaping this dynamic field, the industrial model stands out as a beacon of modern architectural design. This article delves deeply into the significance of the industrial model, showcasing its advantages, applications, and its transformative impact on the architecture industry, particularly for architects.
Understanding the Industrial Model
The industrial model refers to an architectural design approach that emphasizes functionality, efficiency, and sustainability. It is characterized by the use of materials, construction methods, and design philosophies that align with industrial practices. This model not only meets the growing demand for aesthetically pleasing structures but also addresses environmental concerns and economic challenges.
Core Principles of the Industrial Model
At its essence, the industrial model is built upon several core principles that encapsulate its innovative spirit:
- Functionality: Design is driven by purpose, ensuring that spaces are optimized for their intended use.
- Sustainability: Emphasizes the use of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient practices.
- Durability: Structures are built to withstand the test of time, utilizing robust materials and construction techniques.
- Flexibility: Spaces are designed to be adaptable, allowing for changes in use without extensive renovations.
The Advantages of the Industrial Model
Embracing the industrial model in architectural design opens the door to numerous advantages that cater to the needs of contemporary society. Here are some key benefits:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
The industrial model offers a distinct cost advantage over traditional architectural approaches. By utilizing mass production techniques and standardized components, architects can significantly reduce costs associated with materials and labor. This economic efficiency is vital for both small businesses and large enterprises aiming to optimize their budgets.
2. Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal
While the industrial design focuses on functionality, it does not compromise on aesthetics. The use of raw materials like steel, concrete, and glass creates a bold, minimalist look that appeals to modern tastes. This aesthetic is particularly popular in urban settings where sleek, contemporary designs signify progress and innovation.
3. Environmental Sustainability
As the world increasingly prioritizes environmental responsibility, the industrial model aligns seamlessly with sustainable practices. Architects can incorporate recycled materials, efficient energy systems, and innovative waste management strategies, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint. Sustainability is not an afterthought; it is central to the industrial model’s ethos.
4. Speed of Construction
The streamlined processes inherent in the industrial model allow for quicker project completion. Prefabrication and modular construction techniques mean that components are built off-site and then assembled on the construction site, significantly reducing construction time. This efficiency is beneficial for both architects and clients aiming to meet tight deadlines.
Applications of the Industrial Model in Architecture
The versatility of the industrial model allows it to be applied across various architectural domains, ranging from residential to commercial and industrial structures. Below are some notable applications:
Residential Architecture
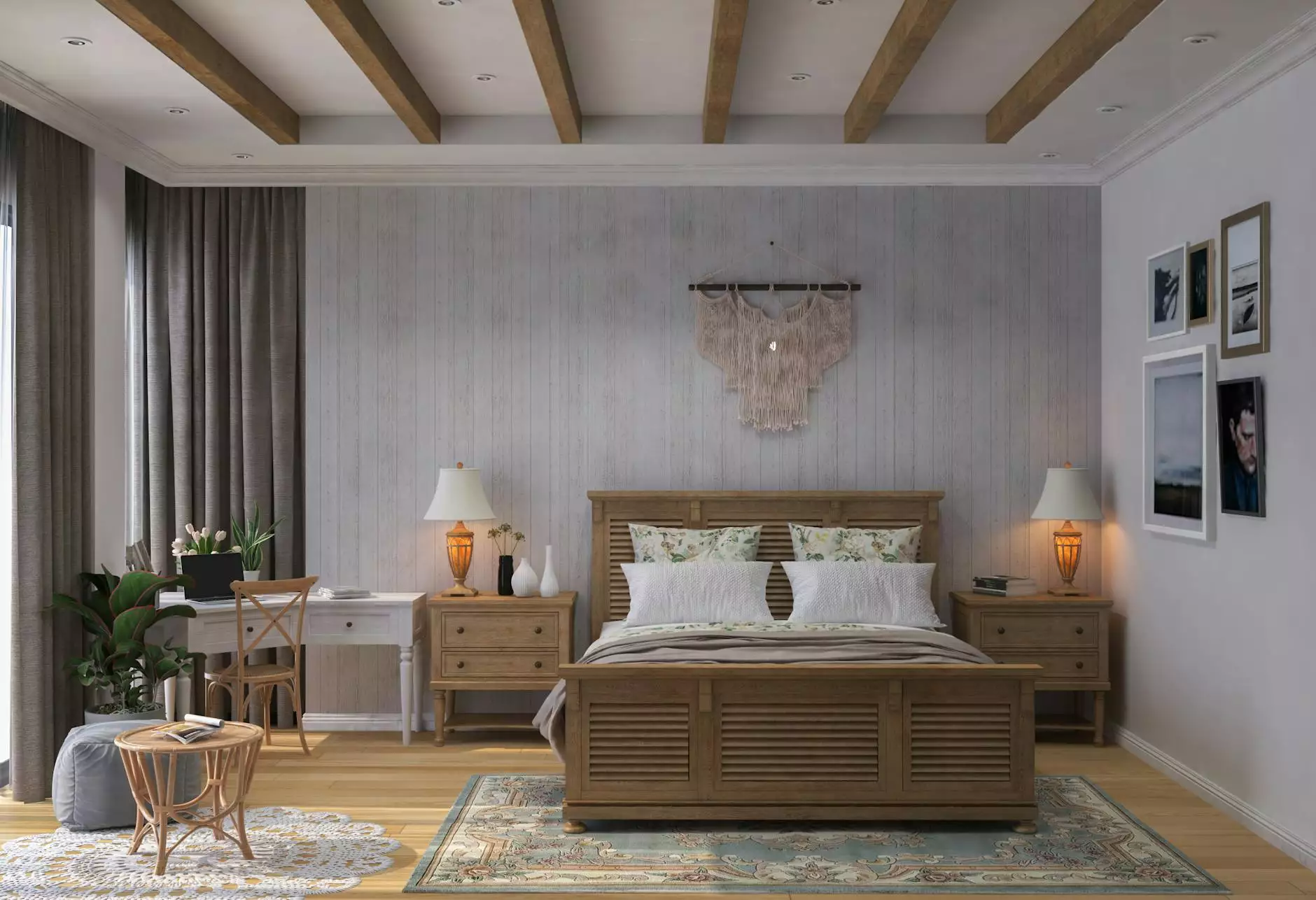
In residential architecture, the industrial model fosters the creation of open-concept living spaces that are both functional and inviting. Features such as exposed beams, ductwork, and large windows provide a sense of spaciousness and connection to the outdoors. These designs often incorporate sustainable materials, making them attractive to environmentally conscious homeowners.
Commercial Structures
The industrial model is particularly beneficial in commercial architecture, where functionality and brand identity are paramount. Businesses can create unique spaces that reflect their ethos while maintaining efficiency. The use of open layouts promotes collaboration and productivity, essential in today’s dynamic work environments.
Industrial Buildings
True to its name, the industrial model is prominently featured in the design of warehouses, factories, and logistical centers. The focus on durability and practicality ensures these structures meet the rigorous demands of industrial operations. Architects can create facilities that enhance workflow, safety, and operational efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations for Architects
While the industrial model presents numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. Architects must navigate several considerations when implementing this approach:
1. Regulatory Compliance
Architects must ensure that their designs comply with local building codes and regulations. This can be particularly challenging in regions with stringent environmental and safety standards. It is essential for architects to stay informed about these regulations to avoid costly delays.
2. Client Expectations
Clients may have preconceived notions of what architectural design should look like. Educating clients about the value and functionality of the industrial model is crucial to aligning their expectations with the innovative approaches that this model offers.
3. Integration of Technology
The industrial model often integrates advanced technologies, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and smart building systems. Architects must familiarize themselves with these technologies to leverage their full potential in design and execution.
The Future of the Industrial Model in Architecture
The future of architectural design looks promising as the industrial model continues to gain traction. As society becomes more aware of environmental issues and the need for functional spaces, architects can expect increased demand for designs rooted in this approach.
Sustainability and Innovation
The intersection of sustainability and innovation will define the evolution of the industrial model. Architects will increasingly rely on renewable energy sources, sustainable materials, and smart technology to create spaces that are not only efficient but also environmentally responsible.
Global Influence
The principles of the industrial model are transcending geographical boundaries. As architects around the world embrace this approach, local adaptations will enhance its applicability in various cultural contexts. This global influence will foster a rich exchange of ideas, ensuring continuous innovation in architectural design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the industrial model is a transformative force in the realm of architecture. Its emphasis on functionality, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal provides architects with a powerful framework to create remarkable structures that meet the demands of modern society. As we look to the future, the principles of the industrial model will undoubtedly shape the next chapter in architectural design, facilitating a harmonious balance between the built environment and the natural world.
Learn More About the Industrial Model
For architects looking to dive deeper into the intricacies of the industrial model, it is crucial to engage with resources that promote continuous learning and innovation. Staying updated on industry trends, attending workshops, and collaborating with other professionals can provide invaluable insights and enhance your design capabilities.
By embracing and championing the industrial model, architects are not merely reacting to current trends but are actively shaping the future of architectural design. Join the movement towards sustainable, efficient, and innovative architecture that resonates with the needs of today's world.